How Long Does Suboxone Stay in Your System? Unveiled Facts!

How Long Does Suboxone Stay in Your System? Suboxone can stay in your system for an average of 3-4 days. It is a medication used to treat opioid addiction and contains a combination of buprenorphine and naloxone.
The duration can vary depending on factors such as metabolism, frequency of use, and dosage. It is important to note that traces of Suboxone can be detected in urine, blood, saliva, and hair follicles during drug testing. Understanding how long Suboxone stays in your system is crucial for individuals undergoing treatment or facing drug screenings.
Proper management and communication with healthcare professionals are essential for a successful recovery journey.

Credit: www.palmerlakerecovery.com
Introduction To Suboxone
Suboxone, also known as Buprenorphine, is a medication used for opioid addiction treatment. It is a combination of buprenorphine and naloxone, which works by reducing withdrawal symptoms and cravings for opioids. Suboxone is a schedule III controlled substance, which means it has a lower potential for abuse and dependence compared to other opioids.
Composition And Use
The composition of Suboxone includes buprenorphine and naloxone. Buprenorphine is a partial opioid agonist that binds to the same receptors in the brain as opioids. However, it produces a weaker effect than full opioids, reducing withdrawal symptoms and cravings. Naloxone, on the other hand, is an opioid antagonist that blocks the effects of opioids. It is added to Suboxone to prevent misuse and abuse of the medication. If you are wondering, “How Long Does Suboxone Stay in Your System,” the presence of buprenorphine and naloxone in your body can be detected for varying durations depending on factors like dosage and individual metabolism.
Suboxone is used as a part of medication-assisted treatment (MAT) for opioid addiction. It is usually prescribed in the form of sublingual tablets or film. The dosage and duration of treatment vary depending on the severity of addiction and individual needs.
Popularity In Treatment
Suboxone has gained popularity in the treatment of opioid addiction due to its effectiveness and safety profile. According to the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA), the number of people receiving buprenorphine treatment increased from 100,000 in 2006 to over 1 million in 2018.
Suboxone is preferred over other medications for opioid addiction treatment due to its lower risk of overdose and withdrawal symptoms. It is also less likely to be abused or diverted compared to full opioids.
In conclusion, Suboxone is a medication used for opioid addiction treatment that includes buprenorphine and naloxone. It is preferred over other medications due to its effectiveness and safety profile. The duration of Suboxone in the system varies depending on several factors, including dosage, duration of use, and individual metabolism.
Credit: www.recoverydelivered.com
Suboxone Absorption And Metabolism
Understanding how Suboxone is absorbed and metabolized in the body can provide insights into how long it stays in your system.
How The Body Processes Suboxone
Suboxone is typically taken sublingually, where it is absorbed through the mucous membranes in the mouth.
Once absorbed, buprenorphine binds to opioid receptors in the brain, reducing withdrawal symptoms.
Naloxone in Suboxone helps prevent misuse by blocking the effects of other opioids.
Factors Influencing Metabolism
Several factors affect how long Suboxone stays in your system:
- Metabolic rate
- Hydration levels
- Liver function
- Frequency of use
Metabolism plays a crucial role in how quickly Suboxone is broken down and eliminated.
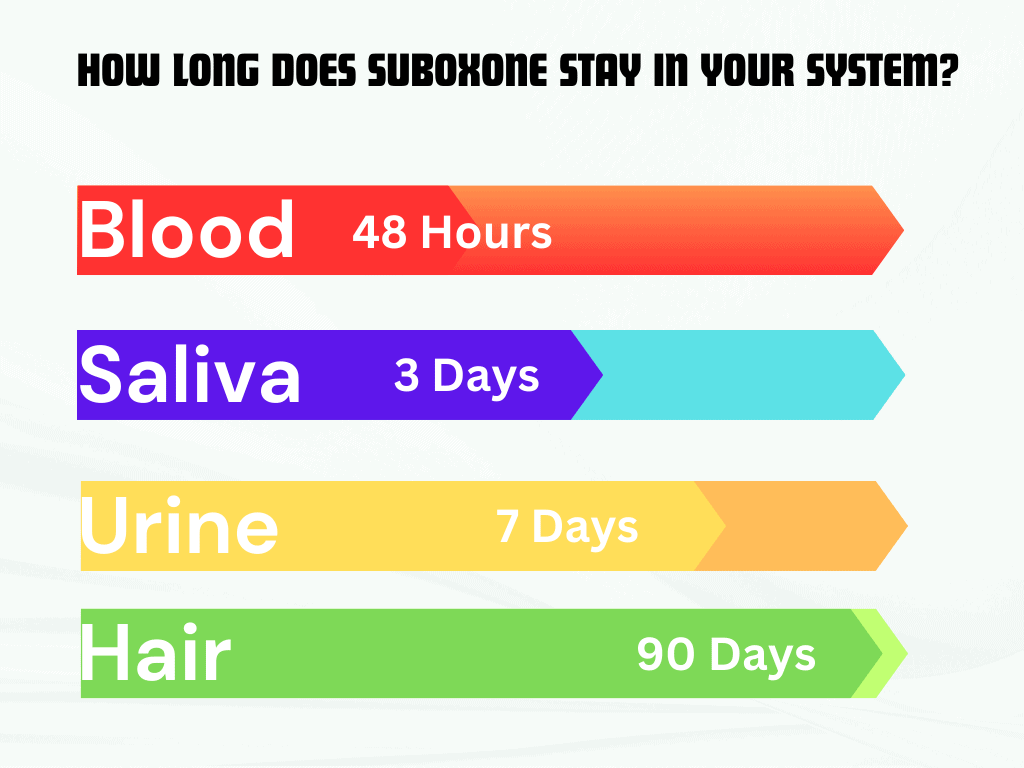
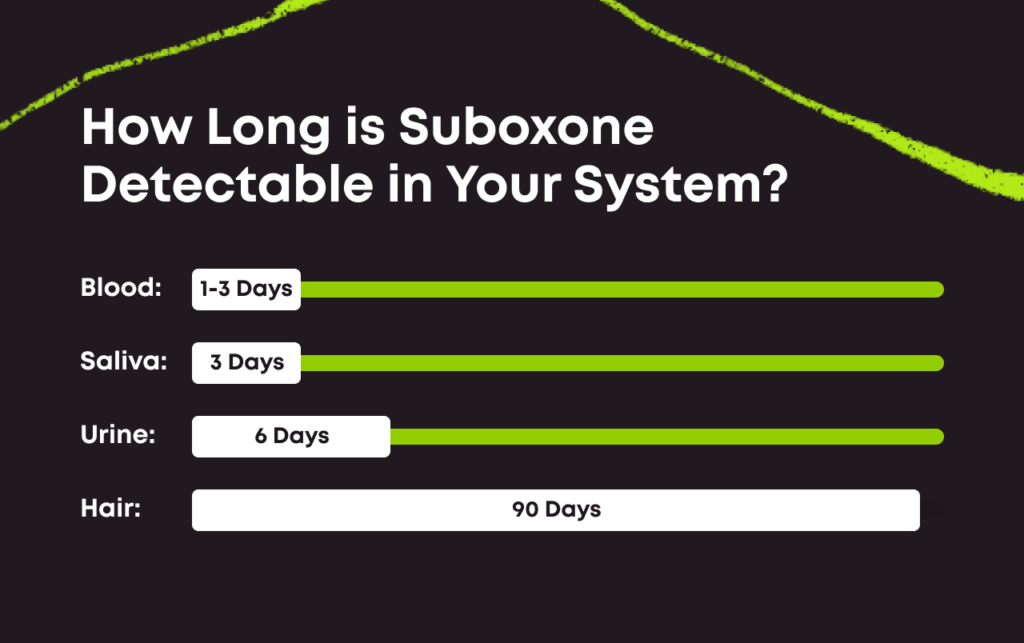
Detection Windows By Testing Methods
When it comes to determining how long Suboxone stays in your system, different testing methods provide varying detection windows. These detection windows refer to the timeframe during which Suboxone can be detected in different bodily fluids or tissues. Here’s a breakdown of the detection windows for Suboxone based on different testing methods:
Urine Tests
Urine tests are commonly used to detect Suboxone in the body. The detection window for Suboxone in urine typically ranges from 2 to 7 days. However, it’s important to note that individual factors such as metabolism, dosage, and frequency of use can influence the duration of detection.
Blood Tests
Blood tests are less frequently used to detect Suboxone, but they can provide accurate results. The detection window for Suboxone in blood is relatively shorter compared to urine tests, typically ranging from 24 to 48 hours. Again, individual factors can affect this timeframe.
Saliva Tests
Saliva tests are becoming more popular due to their non-invasive nature. The detection window for Suboxone in saliva is relatively shorter, usually ranging from 1 to 4 days. However, it’s important to note that the sensitivity of saliva tests may vary, and detection windows can be influenced by individual factors.
Hair Follicle Tests
Hair follicle tests are known for their longer detection windows compared to other testing methods. Suboxone can be detected in hair follicles for up to 90 days or even longer. This is because drug metabolites become embedded in the hair shaft as it grows.
It’s essential to understand that these detection windows are approximate ranges and can vary based on individual factors. It’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional or testing facility for accurate information regarding Suboxone detection windows.
Factors Affecting Suboxone Duration In The System
Factors such as metabolism, dosage, and frequency of use impact how long Suboxone remains detectable in the body. Generally, Suboxone can be detected in urine for up to 2-4 days, in saliva for 1-5 days, and in blood for around 24 hours.
Factors Affecting Suboxone Duration in the System Suboxone is a medication commonly used to treat opioid addiction. It contains buprenorphine and naloxone, which work together to reduce withdrawal symptoms and cravings. When taking Suboxone, it is important to consider the factors that can affect how long it stays in your system. These factors include dosage and frequency, individual metabolism, overall health, and lifestyle.
Understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions about your treatment plan. Dosage and Frequency The dosage and frequency of Suboxone can impact how long it stays in your system. Generally, the higher the dose and the more frequently it is taken, the longer it will take for the medication to be eliminated from your body. For instance, a person taking a lower dose of Suboxone every other day may have a shorter duration of the medication in their system compared to someone taking a higher dose every day. Individual Metabolism Individual metabolism is another important factor to consider when determining how long Suboxone will remain in your system.
Metabolism refers to how your body breaks down and eliminates substances. People with a faster metabolism may eliminate Suboxone more quickly than those with a slower metabolism. Factors that can influence metabolism include age, weight, and genetics. Overall Health and Lifestyle Your overall health and lifestyle can also impact how long Suboxone stays in your system. For instance, if you have a healthy liver and kidney function, you may eliminate the medication more efficiently. On the other hand, if you have liver or kidney disease, it may take longer for the medication to be eliminated. Lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, and hydration can also influence how long Suboxone stays in your system.
In conclusion, the duration of Suboxone in your system is influenced by several factors, including dosage and frequency, individual metabolism, overall health, and lifestyle. Understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions about your treatment plan and ensure that you are getting the most benefit from your medication. If you have any concerns or questions about Suboxone, it is important to speak with your healthcare provider.
Suboxone’s Half-life Explained
Understanding Suboxone’s half-life is essential for individuals undergoing treatment and for those who want to know more about the drug’s effects. Suboxone’s half-life refers to the time it takes for half of the drug to be eliminated from the body. This plays a crucial role in determining how long the drug remains detectable in the system.
Definition And Significance
Suboxone’s half-life is the period required for the concentration of the drug in the bloodstream to decrease by 50%. It is an important factor in understanding the duration of Suboxone’s effects and its potential for accumulation in the body. Additionally, it influences the timing of subsequent doses and the process of discontinuation.
Calculating Half-life
The half-life of Suboxone is influenced by various factors, including an individual’s metabolism, liver function, and dosage. As a result, it can vary among different people. However, the average half-life of Suboxone is approximately 24 to 42 hours. This means that it takes around 1-2 days for half of the drug to be eliminated from the system.
Impact Of Suboxone On Health
Suboxone is a medication commonly used in the treatment of opioid addiction. While it can be beneficial in helping individuals overcome their addiction, it is important to understand the impact it can have on one’s health. Both short-term and long-term effects need to be considered to ensure the overall well-being of the individual.
Short-term Effects
In the short-term, Suboxone can produce various effects on the body. These effects may include:
- Relief from withdrawal symptoms
- Reduction in cravings for opioids
- Improved mood and overall well-being
- Increased energy and motivation
- Enhanced focus and concentration
It is important to note that these effects may vary from person to person and depend on factors such as dosage and individual response to the medication.
Long-term Effects
When used in the long term, Suboxone can have both positive and negative effects on health. Some potential long-term effects include:
- Reduced risk of relapse and overdose
- Improved social functioning and quality of life
- Decreased criminal behavior associated with addiction
- Increased stability and ability to maintain employment
- Enhanced relationships with family and friends
However, it is essential to monitor the long-term use of Suboxone, as it can also lead to certain health concerns. These may include:
- Physical dependence and withdrawal symptoms upon discontinuation
- Potential side effects such as constipation, nausea, or insomnia
- Interactions with other medications or substances
- Risk of misuse or abuse
Regular check-ups and open communication with healthcare professionals are crucial in managing any potential risks associated with long-term Suboxone use.
Legal And Medical Considerations Of Suboxone Use
Suboxone is a controlled substance, requiring a valid prescription for legal use.
It is regulated by the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) due to its potential for misuse.
Physicians must follow specific guidelines when prescribing Suboxone to patients.
Employers may conduct drug tests to detect Suboxone in an individual’s system.
Drug testing policies vary depending on the organization and industry.
Individuals prescribed Suboxone should inform employers to avoid misunderstandings.
Credit: www.bicyclehealth.com
Navigating Suboxone Treatment
When starting a Suboxone treatment, it’s essential to have a clear plan in place. Navigating through the process can be overwhelming, but with the right information and support, it becomes more manageable.
Choosing The Right Treatment Plan
Selecting the appropriate treatment plan is crucial for successful Suboxone therapy. Factors to consider include dosage, duration, and individual needs.
- Consult with a medical professional for personalized guidance.
- Evaluate different treatment options available.
- Ensure the plan aligns with recovery goals.
Support And Resources
Access to support and resources is integral to the Suboxone treatment journey. Building a strong network can greatly enhance the recovery process.
- Join support groups for encouragement and motivation.
- Engage in therapy sessions for emotional well-being.
- Stay connected with healthcare providers for monitoring progress.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Does Suboxone Stay In Your System?
Suboxone can be detected in urine for 2-4 days, in blood for 24-60 hours, and in saliva for 1-10 days. Factors such as metabolism and dosage can influence the duration.
What Factors Affect Suboxone’s Duration In The Body?
Metabolism, dosage, frequency of use, and individual body characteristics can impact how long Suboxone stays in the system.
Can Suboxone Show Up In A Drug Test?
Yes, Suboxone can be detected in drug tests. It is advisable to inform the tester about Suboxone usage before the test.
How Does The Body Eliminate Suboxone?
The body primarily eliminates Suboxone through urine, while a smaller portion is excreted through feces.
Conclusion
Understanding how long Suboxone stays in your system is essential for managing its effects. Whether you’re taking it for pain or addiction treatment, knowing its duration can help you make informed decisions. Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance on Suboxone use and its impact on your body.





