How Do Peanuts Grow? Unearthing the Fascinating Process

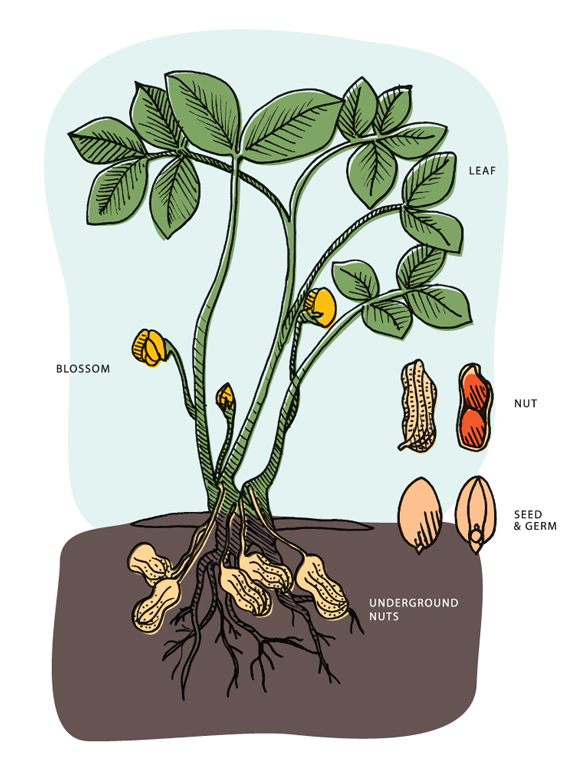
Peanuts grow underground, starting as a flower that wilts and buries itself to mature. Peanuts belong to the legume family and are actually not nuts but legumes.
This versatile crop is a staple in many cuisines worldwide, loved for its rich flavor and nutritional benefits. Peanuts require warm temperatures to thrive and are commonly grown in sandy soil. The plants flower above ground, then bend down, burying the pods in the soil to ripen.
Understanding how peanuts grow can help appreciate the process of cultivating this popular and nutritious legume. Let’s delve deeper into the fascinating journey of peanut cultivation and discover the various stages involved in their growth.

Credit: www.thetreecenter.com
The Lifecycle Of A Peanut Plant
Peanuts undergo a fascinating lifecycle, starting as seeds planted in well-drained soil. As the plants grow, they develop flowers that self-pollinate and eventually form pegs that penetrate the ground. The pegs then develop into pods, containing the peanuts we know and love.
Peanuts are a fascinating crop to grow, as they undergo a unique lifecycle from seed to harvest. The peanut plant is a legume that grows best in warm climates with sandy soil. In this post, we’ll take a closer look at the lifecycle of a peanut plant, from its early stages as a seed to its final maturation.
From Seed To Sprout
The lifecycle of a peanut plant begins with the seed, which is planted in the soil during the spring. If you’re wondering, “How Do Peanuts Grow?”, it all starts with a unique seed composed of two parts: the seed coat and the embryo. The seed coat is hard and protective, while the embryo is the tiny plant that will eventually grow into a mature peanut plant. Once the seed is planted, it begins to absorb moisture from the soil and germinate. The embryo sends out a tiny root, which anchors the plant into the ground, and a shoot, which grows upward toward the sun. As the shoot grows, it breaks through the soil’s surface and begins to form leaves.
Flowering And Pegging
After a few weeks, the peanut plant begins to flower. The flowers are small and yellow, and they grow in clusters near the base of the plant. As the flowers bloom, they produce a structure called a peg, which grows downward into the soil. The peg is an important part of the peanut plant’s lifecycle, as it is where the peanuts themselves will eventually grow. The peg grows down into the soil, and as it does, it begins to form a small pod. The pod is where the peanut will develop, and it will eventually grow to be a few inches long.
As the peanut grows, it pulls nutrients from the soil and sunlight from the sun. It takes about four months for the peanut to mature fully. When the peanut is ready to be harvested, the plant is pulled from the ground, and the peanuts are removed from the pods. In conclusion, the lifecycle of a peanut plant is an intricate and fascinating process. From its early stages as a seed to its final maturation as a peanut, the plant undergoes many changes and adaptations to produce the delicious and nutritious snack we all love.
Peanuts: A Unique Botanical Wonder
Peanuts are a fascinating botanical marvel that captivates curious minds with their unique growth process. Despite being categorized as legumes, peanuts possess distinctive characteristics that set them apart from other leguminous plants.
Not Your Typical Legume
Peanuts, scientifically known as Arachis hypogaea, are not your conventional legume. Unlike typical legumes that grow underground, peanuts exhibit an extraordinary growth pattern that intrigues both botanists and enthusiasts alike.
A Closer Look At Peanut Anatomy
Delving into the anatomy of peanuts unveils their exceptional characteristics. The peanut plant, which belongs to the Fabaceae family, undergoes a remarkable transformation as it progresses through its growth stages.
Cultivating Peanuts: The Farmer’s Role
When it comes to cultivating peanuts, farmers play a crucial role in ensuring a successful harvest. From choosing the right soil to implementing crop rotation, their expertise is essential in growing healthy peanut crops. Let’s explore the various aspects of the farmer’s role in peanut cultivation.
Choosing The Right Soil
Growing peanuts requires a specific type of soil that provides the ideal conditions for their development. Farmers meticulously select soil with adequate drainage and a pH level between 5.8 and 6.2, ensuring optimal nutrient absorption for the plants. The sandy loam soil texture is considered most suitable, as it allows the peanuts to develop properly while preventing excessive moisture retention.
The Importance Of Crop Rotation
Crop rotation plays a vital role in peanut cultivation, benefiting both the plants and the soil. By rotating peanuts with other crops, farmers can break the cycle of diseases and pests that specifically target peanuts. This practice also helps replenish the soil’s nutrients, as different crops have varying nutrient requirements. For example, planting legumes, such as soybeans, in rotation with peanuts helps fix nitrogen levels in the soil, improving overall soil fertility.
Moreover, crop rotation reduces the risk of soil erosion and enhances its structure, promoting healthier root development for the peanuts. By diversifying the crops grown in the same field, farmers can maintain the long-term sustainability of their peanut cultivation.
Overall, the farmer’s role in cultivating peanuts is crucial for ensuring a bountiful harvest. By carefully selecting the right soil and implementing effective crop rotation practices, they create the optimal conditions for peanuts to grow and thrive. Their expertise and dedication contribute to the production of high-quality peanuts that make their way into our favorite snacks and dishes.
Planting The Seeds Of Success
Seasonal Timing For Planting
Peanuts thrive in warm climates with a minimum of 120 frost-free days.
Seed Depth And Spacing
Plant peanuts 1-2 inches deep and 6-8 inches apart in well-draining soil.
Nourishment And Care For Growing Peanuts
When nurturing peanuts, proper care and attention are vital for a successful harvest. Let’s delve into essential aspects of nourishment and care for growing peanuts.
Irrigation Techniques
Watering peanuts is crucial for optimal growth and yield. Implementing efficient irrigation techniques ensures that the plants receive adequate moisture.
Weed And Pest Management
Controlling weeds and pests is essential to protect peanut plants from damage. Proper management techniques help maintain plant health and maximize productivity.
The Underground Development
The Underground Development of peanuts is an interesting process. These legumes grow underground, and farmers have to wait for the perfect time to harvest them. The growth of peanuts is dependent on soil, temperature, and moisture.
Peanuts undergo a unique underground development process.
Pegging: The Key To Peanut Formation
During pegging, the peanut plant forms small pegs that grow downwards. These pegs penetrate the soil to find the ideal spot for pod development.
Root Growth And Nutrient Uptake
The roots of peanut plants grow deeply into the soil. This allows them to access essential nutrients and water. Peanuts have a fascinating underground growth cycle.
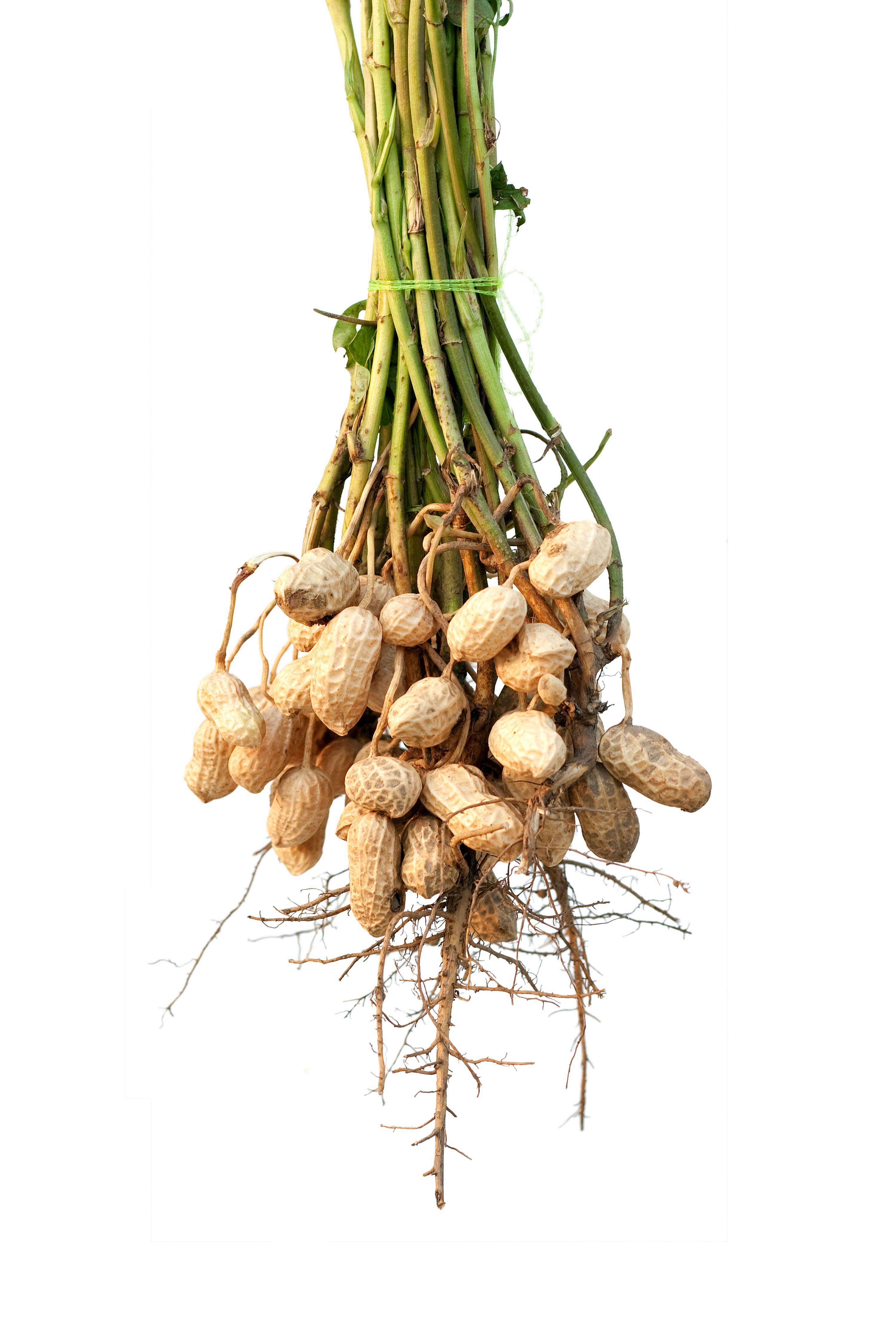
Harvesting: Unearthing The Peanut Crop
When it’s time to reap the peanut crop, a crucial process begins. Harvesting peanuts involves a series of steps that culminate in unearthing the precious legumes.
Determining Harvest Time
Inspect the plant for signs of maturity like yellowing leaves.
Check the pods by gently pressing them for firmness.
Choose the optimal time when most pods are mature.
Mechanics Of Peanut Harvesting
Start by uprooting the entire plant from the soil.
Shake off excess soil to expose the peanuts underground.
Collect the peanuts and allow them to dry before further processing.
Credit: www.flpeanuts.com
Post-harvest: From Ground To Gourmet
After the peanuts have been harvested, the post-harvest process begins to transform these humble legumes into a delicious gourmet treat. The post-harvest phase involves essential steps such as drying and curing peanuts, as well as quality control and processing. Let’s explore each of these steps in detail.
Drying And Curing Peanuts
Once the peanuts are harvested, they contain a high moisture content that needs to be reduced to prevent spoilage. Drying the peanuts is a crucial step in the post-harvest process. The peanuts are spread out in thin layers to allow air circulation and are left to dry naturally. This process typically takes about one to two weeks.
After the peanuts have dried, they undergo curing, which further enhances their flavor and shelf life. Curing involves storing the peanuts in well-ventilated structures for an extended period. During this time, the peanuts continue to lose moisture and develop their characteristic taste and texture.
Quality Control And Processing
Quality control plays a vital role in ensuring that only the finest peanuts make it to our tables. The harvested peanuts go through rigorous inspection to eliminate any damaged or defective nuts. This step ensures that only high-quality peanuts are selected for further processing.
Once the peanuts pass the quality control stage, they are ready for processing. Depending on their intended use, peanuts can be processed in various ways. Some common processing methods include roasting, blanching, grinding into peanut butter, or pressing for oil extraction.
Roasting is a popular method that brings out the natural flavors of peanuts, providing a deliciously crunchy snack. Blanching involves removing the peanut skins, resulting in a smooth and creamy texture. Grinding peanuts into butter creates a versatile spread loved by many. Lastly, pressing peanuts for oil extraction yields a nutritious and flavorful cooking oil.
From the ground to gourmet, the post-harvest process transforms peanuts into a wide array of delicious and nutritious products. Drying and curing ensure the proper preservation of peanuts, while quality control and processing guarantee only the finest peanuts reach our plates. So the next time you enjoy a handful of roasted peanuts or indulge in a jar of creamy peanut butter, remember the journey they underwent to become the delightful treat you love.
Environmental Impact And Sustainable Practices
The environmental impact of peanut cultivation is a critical consideration in today’s agricultural landscape. Sustainable practices are essential to minimize the ecological footprint of peanut farming. Let’s delve into two key sustainable practices: conservation tillage and integrated pest management.
Conservation Tillage
Conservation tillage, also known as no-till farming, involves minimizing soil disturbance during planting and cultivation. This method helps to prevent soil erosion and maintains soil structure, reducing the risk of nutrient runoff. By preserving the soil’s natural integrity, conservation tillage promotes a healthier ecosystem and mitigates the environmental impact of peanut cultivation.
Integrated Pest Management
Integrated pest management (IPM) is a sustainable approach that focuses on preventing and managing pest infestations while minimizing environmental impact. By integrating various pest control methods such as biological controls, crop rotation, and targeted pesticide applications, farmers can effectively manage pest populations while minimizing the use of harmful chemicals.
Peanuts In Cuisine And Culture
Peanuts, known for their versatility, play a significant role in various cuisines globally. Cultivated underground, peanuts thrive in warm climates, developing beneath the soil. This unique growth process makes peanuts a valuable and nutritious crop in both cuisine and culture.
Peanuts are an important crop worldwide, not only for their nutritional value but also for their cultural significance. From Africa to Asia, peanuts have found their way into various cuisines, adding flavor and texture to dishes. In this post, we will explore the culinary uses of peanuts and their role in popular culture.
Culinary Uses Around The World
Peanuts are a versatile ingredient used in many different cuisines. In Africa, groundnuts (as they are commonly known) are used in stews and sauces, such as the popular West African dish, groundnut soup. In Asia, peanuts are used in stir-fries, curries, and sauces, such as the famous Indonesian dish, gado-gado. In America, peanuts are a popular snack food, but they are also used in savory dishes like peanut butter and jelly sandwiches, and in desserts like peanut butter cookies and pies.
Peanuts In Popular Culture
Peanuts have also found their way into popular culture, from literature to movies to music. In the United States, the comic strip Peanuts, created by Charles M. Schulz, features the beloved character, Snoopy, who is often seen eating peanuts. In the movie, Forrest Gump, the main character famously says, “Anyway, like I was sayin’, shrimp is the fruit of the sea.
You can barbecue it, boil it, broil it, bake it, saute it. Dey’s uh, shrimp-kabobs, shrimp creole, shrimp gumbo. Pan fried, deep fried, stir-fried. There’s pineapple shrimp, lemon shrimp, coconut shrimp, pepper shrimp, shrimp soup, shrimp stew, shrimp salad, shrimp and potatoes, shrimp burger, shrimp sandwich. That- that’s about it.” But he also mentions peanuts as one of his favorite foods. In music, the song “Peanut Butter Jelly” by Galantis is a catchy tune that references the classic sandwich.
In conclusion, peanuts have a rich cultural history and have become a staple ingredient in many cuisines around the world. Their versatility and delicious flavor make them a popular choice for everything from snacks to desserts. So, the next time you enjoy a peanut butter and jelly sandwich or a stir-fry with peanuts, remember the cultural significance of this humble legume.

Credit: www.countryliving.com
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Does It Take For Peanuts To Grow?
Peanuts typically take about 120 to 150 days to grow from planting to harvesting. The exact time may vary depending on the variety of peanuts and the growing conditions. It is important to monitor the plants and harvest them when the peanuts have matured.
What Are The Optimal Growing Conditions For Peanuts?
Peanuts thrive in warm climates with temperatures between 70 and 90 degrees Fahrenheit. They require well-drained soil with a pH level between 5. 8 and 6. 2. Adequate sunlight, about 6 to 8 hours per day, is also crucial for their growth.
Regular watering and proper fertilization are essential for optimal peanut growth.
Can Peanuts Grow In My Backyard Garden?
Yes, peanuts can be grown in a backyard garden as long as the necessary growing conditions are met. They require a sunny spot, well-drained soil, and proper care. However, peanuts have a long growing season and need a significant amount of space due to their spreading nature.
It’s best to check with your local agricultural extension office for specific guidelines in your area.
Conclusion
After learning about the process of how peanuts grow, it is clear that these legumes require a unique and specific environment to thrive. From the soil type to the amount of water and sunlight, each factor plays a crucial role in the growth of this popular snack.
However, with proper care and attention, anyone can cultivate their own peanuts right in their backyard. Understanding the growth process of peanuts not only sheds light on the complexity of agriculture but also encourages individuals to appreciate the hard work and dedication that goes into producing our food.





