How Much is a Cow Worth? Unveil the Economic Impact

A cow can cost anywhere from $1,000 to $3,000 on average. The price can vary based on factors like breed, age, and location.
Cows are an integral part of the agricultural industry, providing milk, meat, and other by-products. They are also commonly raised as livestock on farms. The cost of a cow can depend on various factors, including its breed. Certain breeds, such as Angus or Holstein, are known for their high-quality meat or milk production and can be more expensive.
Age is another determining factor, as younger cows may be more valuable for breeding purposes. Additionally, the location of the purchase can influence the price, as prices can vary between different regions. Overall, the cost of a cow can vary significantly, but it is essential to consider factors like breed, age, and location when determining the price.
The Value Of A Cow
How Much is a Cow? The value of a cow varies based on factors like breed, age, and market demand. Generally, a cow can cost anywhere from a few hundred to several thousand dollars, with dairy cows typically priced higher than beef cattle. Additionally, factors like health, size, and purpose also influence the price of a cow.
Factors Influencing Bovine Economics
The value of a cow is a complex concept that involves numerous factors. Bovine economics is influenced by various aspects such as age, gender, breed, weight, and market demand. Farmers, ranchers, and livestock traders must take all these factors into consideration when determining the value of their cattle.
Price Variations Across Breeds
Price variations across breeds are significant due to the differing characteristics of each breed. Some breeds are known for their high-quality meat, while others are bred for their milk production or their ability to thrive in harsh climates. As a result, the price of a cow can vary widely depending on its breed. Here is a table showcasing the average prices of some of the most popular cattle breeds in the United States:
| Breed | Average Price |
|---|---|
| Angus | $1,500-$3,000 |
| Hereford | $1,200-$2,500 |
| Limousin | $1,500-$3,500 |
| Charolais | $1,800-$3,500 |
| Holstein | $1,000-$2,500 |
It’s important to note that these prices are only estimates and can vary depending on the location, market demand, and other factors. In conclusion, the value of a cow is not a straightforward concept. It’s influenced by various factors such as breed, age, gender, weight, and market demand. Farmers and ranchers must take all these factors into account when determining the value of their cattle.
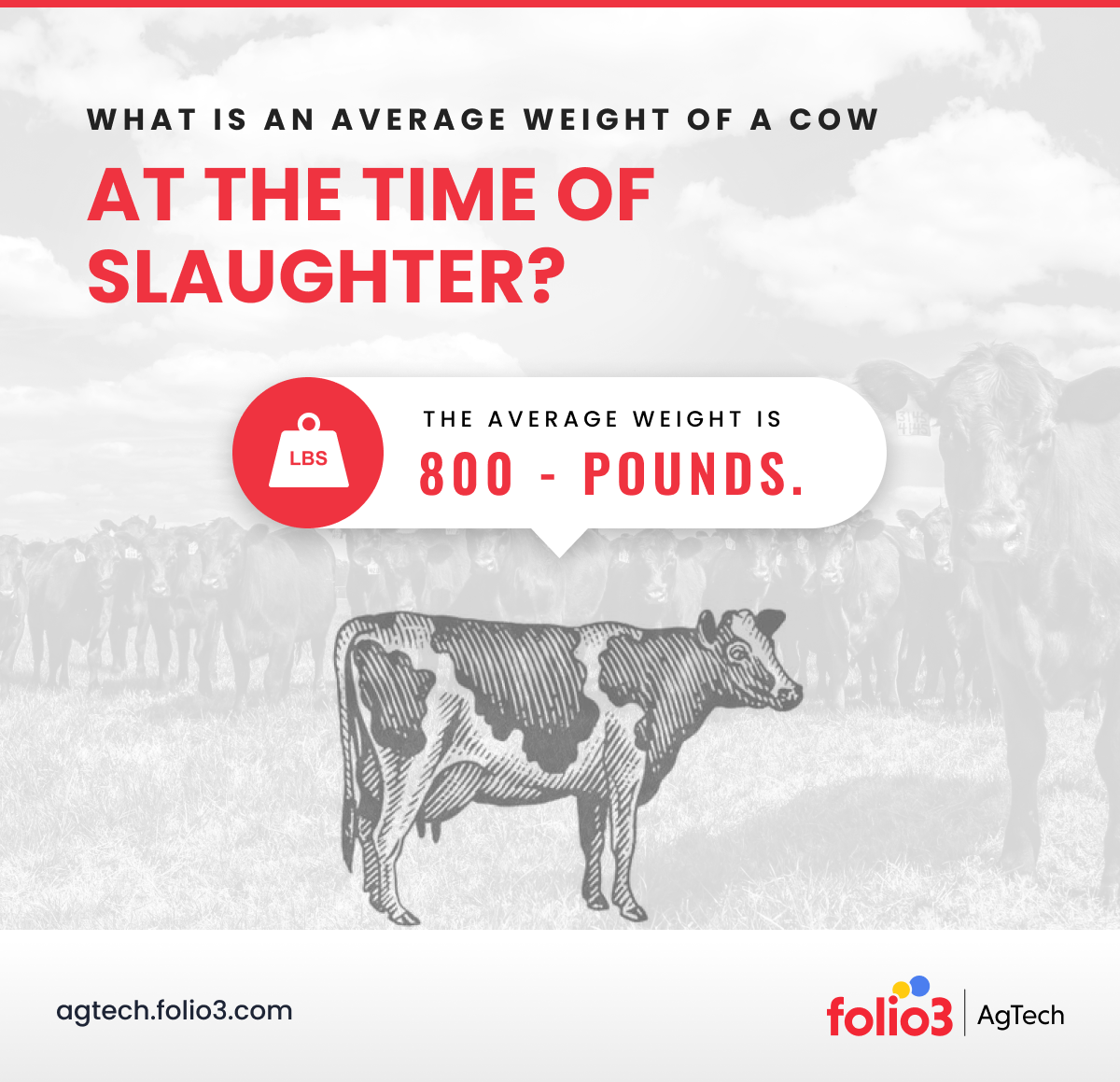
Credit: agtech.folio3.com
Cows In Agriculture
Cows play a vital role in agriculture, contributing significantly to both dairy production and the beef industry.
Role In Dairy Production
Cows are primary sources of milk and dairy products.
- Milk provides essential nutrients like calcium and protein.
- Dairy products include cheese, butter, and yogurt.
Beef Industry Contributions
Cows are a cornerstone of the beef industry.
- They supply meat for consumption and various beef products.
- Cattle breeding and raising are essential for beef production.
Global Market Trends
In the current global market trends, the price of a cow varies based on factors like breed, age, and market demand. Farmers closely monitor these fluctuations to determine the best time to buy or sell their livestock.
The global market for cows is subject to various trends and factors that impact the prices and availability of these animals. Two significant factors that influence the cow market are the
Impact Of Export And Import
The cow market is heavily influenced by international trade, with both exports and imports playing a crucial role. Countries that have a surplus of cows often export them to meet the demand in other regions. This movement of cows across borders can have a significant impact on the global market. Exporting cows allows surplus-producing countries to capitalize on their production capabilities, while importing countries gain access to a wider variety of breeds and genetic diversity. This exchange helps maintain a healthy balance between supply and demand in the global cow market. However, it also means that market prices can be influenced by factors such as trade policies, transportation costs, and political stability.
Price Fluctuations
Price fluctuations are a common occurrence in the cow market. Various factors contribute to these fluctuations, including changes in feed costs, weather conditions, disease outbreaks, and shifts in demand and supply. Understanding these price fluctuations is essential for both buyers and sellers in the cow market. For example, if the cost of feed increases, farmers may need to adjust their pricing to cover the additional expenses, leading to higher cow prices.
Similarly, if a disease outbreak affects the cow population in a particular region, it can decrease the supply and potentially drive prices up. It is important to note that price fluctuations can occur both at the local and global level. Local factors, such as changes in land availability or regulations, can impact prices in specific regions. However, global trends, such as changes in demand from emerging markets or shifts in trade policies, can have a broader impact on cow prices worldwide.
In conclusion, understanding the global market trends in the cow industry is crucial for stakeholders to make informed decisions. The impact of export and import, along with price fluctuations, significantly influence the availability and pricing of cows. By keeping a close eye on these trends, industry players can adapt their strategies and navigate the dynamic cow market more effectively.
Cultural And Historical Significance
With its rich cultural and historical significance, the value of a cow goes beyond its price tag. From ancient rituals to traditional farming practices, cows have played a pivotal role in shaping societies across the globe. Their presence symbolizes prosperity, sustenance, and a connection to ancestral traditions.
Explore the fascinating world of cow symbolism and the impact it has had on cultures throughout history.
Cows have been an integral part of human civilization since ancient times. Their cultural and historical significance is profound and has been recognized across various cultures and religions. Let’s delve deeper into the role of cows in tradition, religion, and historical trade and barter.
Cows In Tradition And Religion
Cows hold a special place in many cultures and religions. In Hinduism, cows are considered sacred and worshipped as a symbol of wealth, strength, and motherly love. They are believed to be the embodiment of the divine and are often depicted in Hindu mythology as the vehicle of various gods and goddesses. Similarly, in Buddhism, cows are revered for their gentle nature and are regarded as symbols of compassion and kindness. The Buddha is said to have compared his teachings to the milk of a mother cow, which nourishes and sustains its young.
Historical Trade And Barter
Cows have also played a significant role in historical trade and barter. In ancient times, cows were used as a form of currency to buy and sell goods. They were also exchanged as gifts during marriages and other ceremonies. In many parts of the world, cows were used as a means of transportation, plowing fields, and providing milk and meat. They were also used to produce leather, which was a valuable commodity in the past.
Today, cows continue to play an important role in agriculture and the economy. They are raised for their milk, meat, and leather, and are an essential source of food and income for many communities around the world. In conclusion, cows have been an integral part of human civilization for centuries. They have held immense cultural and historical significance, and continue to play an important role in our lives today.
Modern Farming Practices
Modern farming practices have evolved significantly, incorporating technological advancements and a shift towards organic farming. These changes have influenced the cost of raising cows, impacting the overall price of a cow in today’s market.
Technological Advancements
The integration of technology in farming has revolutionized the way cows are raised. Automated feeding systems and milking robots have enhanced efficiency, while GPS-guided tractors have optimized land management.
Organic Vs. Conventional Farming
The debate between organic and conventional farming methods continues to shape the industry. Organic farming emphasizes sustainable practices and natural feed, while conventional methods rely on pesticides and genetically modified organisms.
Economic Challenges
Economic challenges can greatly impact the cost of a cow, affecting its market value and affordability for farmers. Fluctuating prices of feed, labor, and land can all influence the overall cost of purchasing and maintaining a cow, posing financial hurdles for agricultural businesses.
Costs Of Raising Cattle
Raising cattle can be a rewarding endeavor, but it comes with its fair share of economic challenges. One of the primary concerns for farmers and ranchers is the cost involved in raising and maintaining a cow. The expenses can vary depending on factors such as the breed, location, and the size of the operation. There are several costs to consider when it comes to raising cattle. These include: 1. Feed: Cows require a substantial amount of feed to grow and produce milk.
The cost of purchasing or producing feed can significantly impact the overall expenses. This includes hay, grain, and other supplements necessary for their nutrition. 2. Housing and Facilities: Providing appropriate housing and facilities for the cattle is essential. This includes barns, fences, and equipment for feeding and watering. The construction and maintenance of these facilities can add up to the overall costs. 3. Veterinary Care: Regular veterinary care is crucial for the health and well-being of the cows. Expenses associated with vaccinations, deworming, and routine check-ups should be factored into the budget. 4. Equipment and Machinery:
Owning or leasing the necessary equipment and machinery for managing the cattle operation is another cost to consider. This includes tractors, trailers, and handling equipment. 5. Labor: The labor required for daily tasks such as feeding, milking, and cleaning can contribute to the overall expenses. Hiring additional help or outsourcing certain tasks may incur additional costs.
Market Risks And Insurance
In addition to the costs of raising cattle, farmers and ranchers also face market risks that can impact their profitability. Fluctuations in cattle prices and market demand can significantly affect the income generated from selling cattle or their products. To mitigate these risks, many farmers opt for insurance coverage. Livestock insurance provides protection against the loss of cattle due to accidents, natural disasters, or disease outbreaks.
It can help farmers recover some of their investment in case of unforeseen circumstances. It’s important for farmers to assess the risks involved and choose appropriate insurance coverage tailored to their specific needs. Insurance premiums will vary based on factors such as the number of cattle, the breed, and the location of the operation. Overall, the economic challenges in raising cattle require careful planning, budgeting, and risk management. By understanding and addressing these challenges, farmers can navigate the complexities of the industry and work towards a sustainable and profitable cattle operation.
Environmental Considerations
A cow’s environmental impact goes beyond its cost. From greenhouse gas emissions to water usage, raising cows has significant effects on the environment. As consumers, it’s important to consider these factors when deciding how much meat to consume and how often.
Sustainability And Cattle Farming
Cattle farming must prioritize sustainability for long-term benefits.
- Sustainable practices reduce environmental impact.
- Efficient resource utilization is key for sustainability.
- Balanced ecosystems support sustainable cattle farming.
Climate Change Impacts
Climate change affects cattle farming and the environment.
- Rising temperatures impact cattle health and productivity.
- Extreme weather events disrupt farming operations.
- Mitigating emissions is crucial for combating climate change.

Credit: ranchr.ag
Future Of Cattle Economics
The future of cattle economics is uncertain, with the price of cows fluctuating based on various factors such as demand, supply, and market conditions. Understanding the current market value of a cow is crucial for cattle farmers and investors alike.
However, predicting the exact cost of a cow can be challenging due to the dynamic nature of the industry.
The future of cattle economics is evolving rapidly with technological advancements.
Innovations In The Industry
Technological innovations are reshaping cattle farming practices. Automation in feeding systems boosts efficiency and reduces labor costs. Genetic engineering enhances cattle breeding for improved productivity.
Predictions For Market Growth
Global demand for beef is projected to increase steadily. Emerging markets show promising growth opportunities for cattle industry. Sustainable practices are key for long-term market sustainability.
Credit: www.quora.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Average Cost Of A Cow?
The average cost of a cow varies depending on factors such as breed, age, and size. Generally, the cost ranges from $1,000 to $2,500 for a dairy cow and $1,200 to $2,000 for a beef cow.
How Much Space Does A Cow Need?
Cows require ample space for grazing and roaming. On average, a cow needs at least 2 acres of pasture land for grazing. Providing sufficient space ensures their comfort and overall well-being.
What Are The Expenses Of Owning A Cow?
Owning a cow entails expenses such as feed, veterinary care, and shelter. Additional costs may include fencing, equipment, and breeding services. It’s essential to factor in these expenses when considering cow ownership.
Conclusion
The cost of a cow depends on various factors such as breed, age, and purpose. Whether for dairy or meat production, it’s essential to consider the initial investment and ongoing expenses. Additionally, understanding the market demand and potential profits is crucial for a successful cattle farming venture.





